This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
AI & Automation in the Contact Centre: driving efficiencies and improving the customer experience
Executive Summary
In this White Paper, FourNet looks at how Artificial Intelligence and Automation can
be utilised to improve internal and external processes for different industry sectors – enhancing customer experience and customer journeys and assisting employees, both inside the workplace and when working remotely.
Artificial Intelligence allows organisations to automate many of the more repetitive tasks in the customer support journey leaving employees to focus on more complex enquiries. This in turn ensures customers are left with higher levels of satisfaction.
Chatbots provide answers to basic questions allowing customers to serve themselves and often removing the need for mundane and repetitive tasks by agents in the contact centre. For more complex issues where customers want to engage with an agent, AI can be used to route an enquiry to an agent with the right skills, thereby increasing first contact resolution, improving agent efficiency and outcomes in the contact centre.
Thanks to FourNet’s sector specific expertise, we are able to address the most common issues by industry sector. This White Paper considers the business drivers and how to build the business case for investing in Artificial Intelligence. We share best insights on how to introduce AI and Automation to ensure improved processes, job satisfaction for employees and improved business outcomes.
Intro
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a huge, complex topic which can impact on many aspects of daily life. In this White Paper we look at how AI can be used to enable customer self service and improve agent efficiency and outcomes in the contact centre. We will look at the business drivers and how to build the business case for investing in Artificial Intelligence; we’ll also share our insights on how to get started with AI and highlight how FourNet can help.
There is a broad array of AI-enabled solutions to improve efficiency, produce cost savings and improve the customer experience, so we have grouped them into four logical categories:
Customer Self Service
Chatbots, natural language Interactive Voice Response (IVRs) and voice authentication give the customer the opportunity to answer their own query without needing to speak to an agent. All self-service options also require a seamless process to handoff the query to an agent.
AI Enabled Assisted Service
This category of solutions uses AI to provide an agent with more information based on the inputs received from customers, predicting potential requests and recommending how to fulfil them, thus empowering agents to handle queries and deliver quicker resolutions to customers. Prediction of customer sentiment also helps agents handle potentially challenging customer issues. These Assisted Service solutions can be particularly relevant for inexperienced agents or where agents are working remotely.
AI for smarter routing an operational insights
AI enabled contact centres can harness the huge processing power of AI to route queries to the right agent using the predictive techniques of Machine Learning. The technology also helps make more streamlined decisions and use sentiment analysis to predict behaviour and improve outcomes.
Driving Agent Efficiency with AI
Artificial Intelligence powered Workforce Optimisation and Quality Management offers huge potential to improve agent performance. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has the ability to automate non-value-added tasks; speeding wrap-up time, increasing the accuracy of data entry and thereby freeing agent time to focus on more value-added tasks.
What is AI
“Artificial Intelligence technologies aim to reproduce or surpass abilities (in computational systems) that would require ‘intelligence’ if humans were to perform them. These include: learning and adaptation; sensory understanding and interaction; reasoning and planning; optimisation of procedures and parameters; autonomy; creativity; and extracting knowledge and predictions from large, diverse digital data.”
In other words, you might say, AI can do more and think faster with greater amounts of information and data than is humanly possible in the same timeframe.
AI is able to extract sentiment from the way people talk. It can understand if you are likely to get angry or upset, using tone and speech analytics, and is then able – if programmed correctly – to deal with those emotions to minimise impact on the customer and business.
Based upon the customer’s history, the context of the call, and previous patterns of similar interactions, AI can predict the most appropriate action to take, potentially handling a tricky customer who it considers likely to get upset. AI can be programmed to head off that anger, perhaps with a sales offer or a new service.
As AI technologies have developed, more human-like traits have been added, such as avatars and speech. That means, for instance, that conversational AI can be made to deal with customer enquiries through a chatbot, which expresses human-like emotions.
Rather than having a rules-based chatbot, AI can be used to switch over to a ‘cognitive’ system (self-learning AI system) allowing for more intelligent prediction and reaction to customer enquiries. Rather than simply directing customers to the correct part of the website or FAQ and route to a customer live chat human agent, it can learn progressively to be able to solve queries on its own and provide a better interactive experience. However it will take time for chatbots to fully enable that and handle all interactions.
Consider how such an ‘intuitive’ capability can improve customer experience while enhancing the reputation of an organisation.
Imagine a scenario where there’s a complex calculation that requires to be done, or a question an agent doesn’t know the answer to, and where the waiting is frustrating for the customer. Now consider giving the agent access to an AI tool which does the complex calculation for the agent, in superfast time, or answers a tricky enquiry without pause. It means less stress for the agent and a quicker response to the customer.
The ‘waiting for answers’ experienced by customers then disappears, while AI assists the agent in performing a task which they wouldn’t have been able to do themselves.
Gartner research shows that AI drastically reduced customer wait times, with chatbots replying within five seconds of customer contact, while typical advisors took 51 seconds.
AI expands the ability of the contact centre to perform better. AI helps to improve efficiency and increase productivity, while allowing staff or contact centre agents to be switched to more relevant tasks. However it takes time for chatbots to learn these skills in order to handle all interactions.
Impact of COVID on AI
Developments in all areas of AI, and uptake of the technology, has been accelerated by COVID-19. Even before the pandemic, analysts were predicting that conversational AI would become as important for an organisation as its own website. Since Coronavirus struck, the functionality offered by AI and automation has taken three of the top five slots in Tech Target’s Customer Experience IT Priorities surveys.
Gartner are predicting that 15% of all customer service interactions will be completely handled by AI this year, an increase of 400% from 2017. They also estimate that 25% of digital workers will use virtual assistants daily. For many organisations, the shift will require an additional digital transformation journey, but it’s one that senior executives will need to grab with both hands.
The pandemic has accelerated digitisation – businesses and customers are doing and wanting to do things via digital that it would have taken years to achieve if COVID-19 hadn’t emerged and changed the way we live our lives. Many customers who would traditionally pick up the phone to speak to an agent were forced to switch to self-service during the early stages of the pandemic when many contact centres were unable to work remotely. The pandemic meant that fewer staff and agents were working in offices and for some businesses this has meant fewer enquiries can be answered as quickly and efficiently as they would have been in the days before the virus hit. Necessity has driven a lasting shift in channel preference for customers.
Contact Centre and Customer Service
What buyers are telling us about their next purchase
Top Project Requirements
1. Enable automated self-service support
2. Improve contact centre agent performance
3. AI Chatbots
4. Support for multiple locations/ remote agents
5. Automate customer-facing processes
Source: Tech Target Contact Centre and Customer Service Confirmed
Consumer Attitudes to AI
Even prior to the pandemic, the ability to hold a ‘conversation’ with technology had also changed our habits for good. Amid the surge in home voice assistants such as Apple’s Siri, and Google’s Alexa, research conducted for Artificial Solutions suggests that there’s a new but growing section of the population – 13% at present – who feel more comfortable using their voice than text, while one in 3 people feel it’s easier to use voice.
There are wide variations by age in the preferred method for contacting a company for an urgent enquiry but on average 50% would prefer to self-serve.
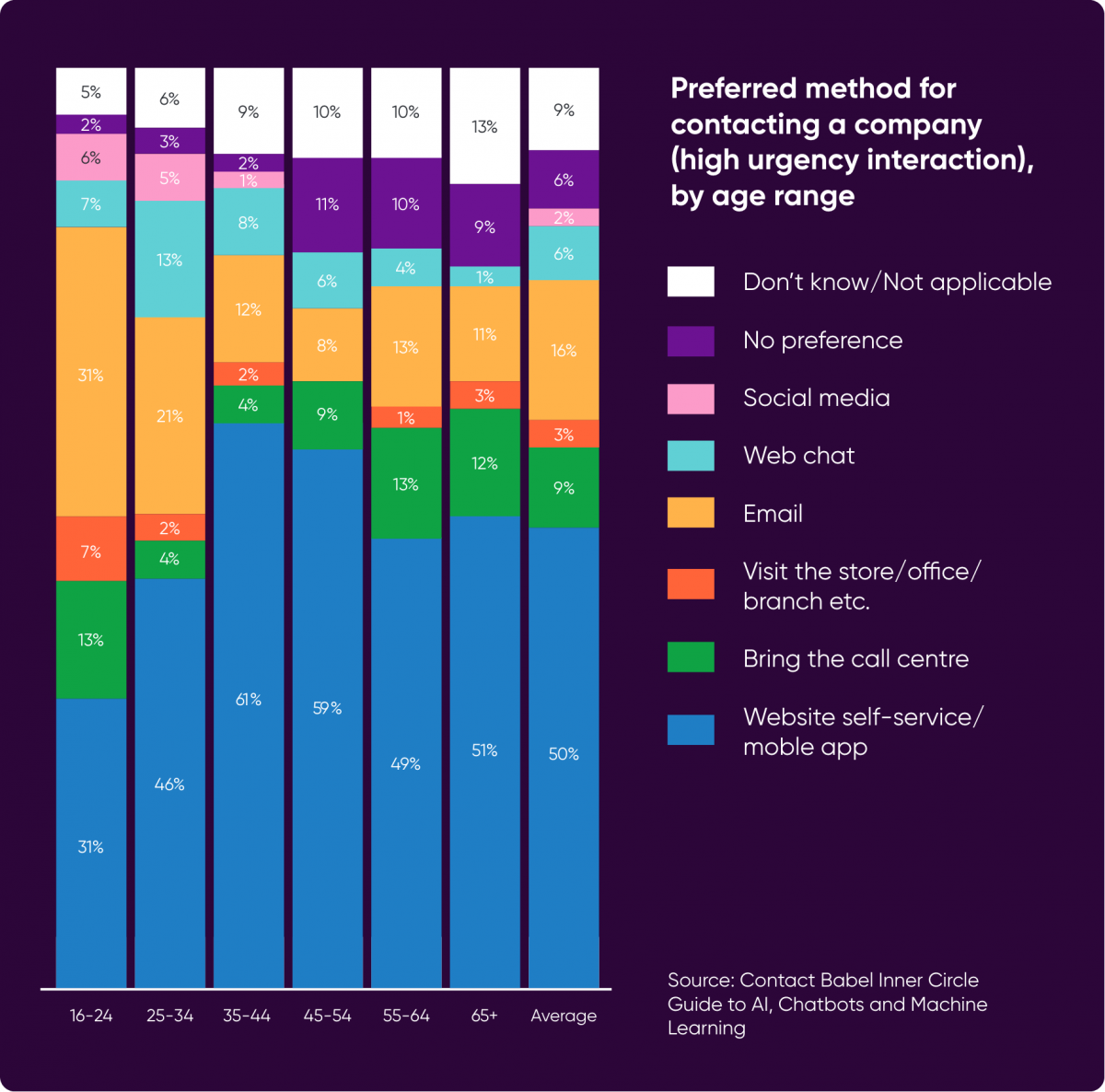
Current Adoption of AI in the Contact Centre
80% Chatbots can answer 80% of standard questions. (IBM)
85% of customer interactions will be handled without human agents by 2021. (Chatbots Life)
90% Bank systems will automate up to 90% of customer interactions using chatbots by 2022. (Chatbots Life)
53% of service organisations are going to use chatbots within the next 18 months. (SalesForce)
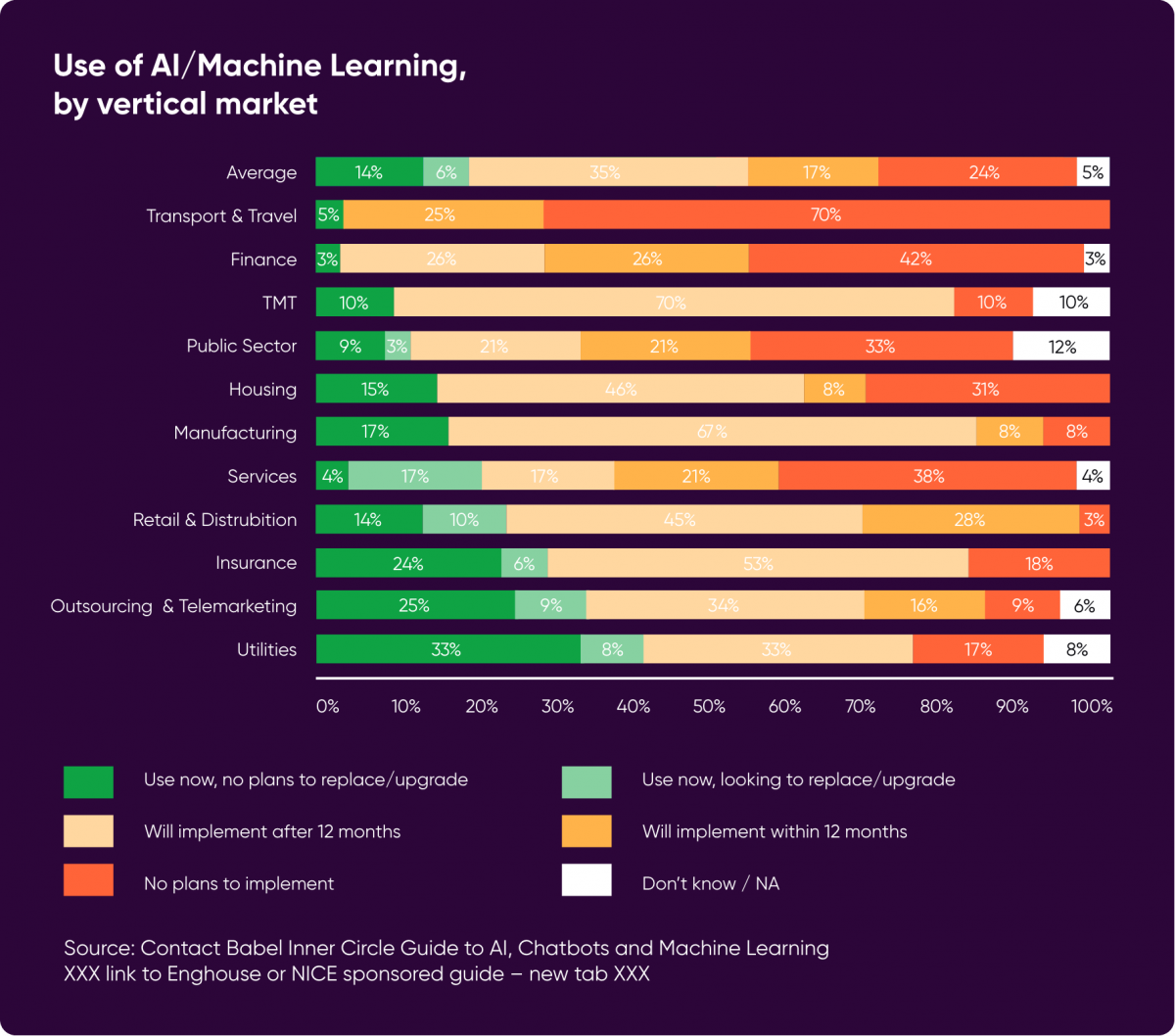
There are a lot of remarkable statistics about the prevalence of AI and chatbots. However, research by Contact Babel indicates that at present only 20% of UK Contact Centres are using AI or Machine Learning and there are massive variances in take-up depending on industry sector:
Business Benefits of AI in the Contact Centre
Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
Artificial intelligence can allow organisations to automate some of the more repetitive tasks in the customer support journey. Chatbots can provide customers with answers to basic questions so that they can serve themselves before seeking the assistance of an agent. Natural Language IVR can enable customers to self-serve via the phone. RPA can automate the completion of basic tasks such as updating a customer’s address across all systems.
For more complex issues where customers want to engage with an agent, AI can be used to route the enquiry to the agent with the right skills to address the issue thereby increasing first contact resolution.
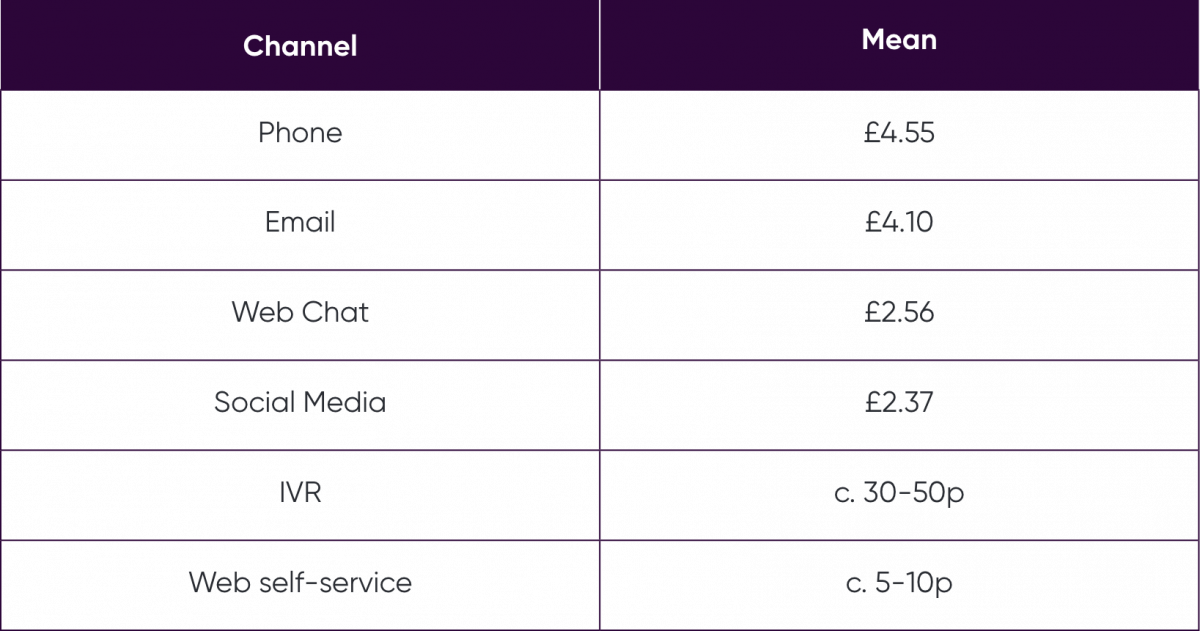
Every contact centre will have their own metrics for measuring the cost per inbound interaction but taking Contact Babel’s mean cost per inbound contact shows how quickly an investment in a web/ app self-service chatbot or Natural Language IVR can pay off.
Cost per inbound interaction
Improve the Customer Experience
Customers have long had the option to vote with their feet (or their keyboard mouse) and switch to a different provider if they don’t get a great experience. Improving the Customer Experience in the post-pandemic world is in the top three priorities for most C-level Execs.
Customers want to know that you understand and care about them. Artificial Intelligence can help you to provide that personalised experience by serving agents with the relevant information to provide a great experience. For instance, as well as ensuring that a call goes through to the person with the best knowledge to handle a call, AI can also provide agents with contextual information about a caller. This means that your agents will be able to see what the customer has had issues with before, which products they’re calling about and more. That way, your customer doesn’t have to repeat their story endless times to get a result.
AI powered sentiment analysis can help agents identify when a conversation is moving in the wrong direction and provide guidance on how to get control of the discussion again.
Improve Agent Performance
AI powered Workforce Optimisation not only enables organisations to accurately predict demand and schedule resources accordingly but can also supercharge Quality Management processes by enabling the monitoring and scoring of 100% of calls automatically rather than just random samples.
Machine learning can then use this huge pool of data to analyse patterns of agent behaviour and characteristics connected with best outcomes, to develop performance and training programs right down to the individual agent level. Gaps in agent knowledge or capabilities can be identified and addressed based on thousands of calls, rather than relying upon manual evaluations which can only process a handful of calls from each agent.
These capabilities are especially important right now with high proportions of agents working from home.
Predict Future Needs
Beyond improving current performance in the contact centre AI can also use the data gathered from day-to-day conversations to make predictions about what a customer might want or need from your company. AI can analyse huge volumes of data rapidly and can spot trends and offer personalised product or service recommendations that we wouldn’t be able to come up with on our own.
AI Solutions in the Contact Centre
In this section we look at the four main categories of AI-enabled contact centre solutions:

Customer Self Service
Most businesses will offer at least some form of customer self-service, for the most part this is a simple FAQ section on the website or an automated IVR. The main objective for AI in most contact centres consists of projects to increase the capability for customers
to self-serve. This not only has the benefit of dramatically reduced costs but also an improved customer experience because of higher real first-contact resolution rates using the customer’s channel of choice.
Chatbots or Virtual Assistants
AI powered chatbots, or virtual assistants, make it simple for organisations to automate customer service interactions and deliver a faster, more personalised experience for customers. Customers can interact with organisations from their preferred device through speech, messaging or visual interfaces and receive an instant, rich and consistent experience. Chatbots connect customers with the answers they need through embedded knowledgebases, from documents, from business applications, and from employees. A chatbot can answer questions and action requests at scale with human levels of understanding and deliver instant answers.
Chatbots, or Virtual Assistants, can deliver immediate responses to customer enquiries 24:7. Utilising AI & Machine Learning an AI powered chatbot can understand conversations no matter how a customer may phrase their enquiry and provides instant responses through automation and integration to live customer service applications.
AI powered chatbots are light years away from the earliest versions of chatbots which could be frustrating and time-consuming for customers. Early chatbots were often only able to respond to very specific input, they were essentially a text-based equivalent of interacting with the old “phone tree” IVR call menus.
How do AI powered chatbots work?
Understanding humans isn’t easy for a machine (it isn’t easy for other humans sometimes).The subtle and nuanced way humans communicate is a very complex task to recreate artificially, which is why chatbots use several natural language principles including Natural Language Processing (NLP), Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Natural Language Generation (NLG). These principles enable chatbots to mimic human conversation. The chatbot can identify the underlying intent behind the text a real person types or speaks, then deliver a response that matches that intent. Chatbots with NLP can now “learn” from past conversations and improve their ability to provide appropriate responses and solutions.
On a simple level, a human interacts with a chatbot. If voice is used, the chatbot first turns the voice data input into text (using Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) technology). Text only chatbots such as text-based messaging services skip this step.
The chatbot then analyses the text input, considers the best response and delivers that back to the user. The chatbot’s reply output may be delivered in any number of ways such as written text, voice via Text to Speech (TTS) tools, or perhaps by completing a task.
Conversational AI bridges the gap between human and computer language and makes two-way communications more natural, without having to configure specific words or phrases. The intelligence comes from the system learning the many different ways that customers communicate their requests to improve the results and understand more.
The most immediate potential of AI powered chatbots in the contact centre is in handling digital enquiries: webchats tend to take longer than phone calls due to agent multi- tasking, and many email response rates take days. Contact Babel’s average cost per inbound contact (see Figure 4) highlights that webchat is not significantly cheaper than voice contact so there is still huge potential for cost saving in automating these engagements.
When the chatbot has low confidence that it has returned the correct result, it is able to escalate the customers query seamlessly to a live chat agent, who then has access to the self-service session history, enabling a greater chance of a successful resolution without repetition.
Impact after 3 months
Natural Language IVR
Telephony self-service currently resolves an average of 29% of inbound enquiries without requiring an agent, according to Contact Babel’s latest research; however, a typical IVR solution can only handle a small number of common enquiries and only works well in cases where the caller has a simple request.
A Natural Language IVR can simply be viewed as a chatbot that customers communicate with through voice, rather than typed text. It needs the capability to handle natural language, to use artificial intelligence to determine intent and provide solutions, and to convert speech to text and back again.
Natural Language IVRs can be used as triage to decide who gets automation and who is directed to an agent based on the profile of the customer, their requirements, circumstances and past outcomes.
As with all forms of customer self-service, an IVR must offer the customer an easy way to opt-out and request to be transferred to a live agent, ensuring all the data that has already been gathered is handed over.
In addition to the standard benefits of enabling customer self-service (24:7 availability, cost reduction, taking pressure off agents etc.) encouraging customers to use Natural Language IVR rather than to press numbers on a keypad generates large amounts of data that can be used to further train AI models.
Voice authentication
Voice authentication is a way to confirm a customer’s identity based on a unique characteristic – their voice. A voice is unique as a fingerprint and consists of a combination of characteristics such as dialect, pitch and speed. Voice authentication is even harder to spoof than fingerprints and can’t be hacked like passwords, making it an extremely secure method of authentication.
Alongside voice authentication, AI can also be used to power “phoneprinting” which focuses on preventing fraud. Phoneprinting collects information about the call being made, such as Calling Line Identifier (CLI), location, the type of phone being used, the phone number’s history, levels of voice distortion, etc. These factors are then scored and the score will then determine the security processes and questions that the agent is required to ask the caller, speeding up the process for genuine callers, and focusing the tightest levels of security on potentially fraudulent calls.
Once the system has a voiceprint, the customer gets a better experience when they call customer service. For example, the interactive voice response (IVR) system can recognise and authenticate their identity, which enables the customer to access self-service tasks like checking account balances. If the customer chooses to speak to an agent, the authentication information can be passed to the agent, which saves time and improves the customer experience because they don’t need to repeat any information.
Benefits:
- Seamlessly voiceprint customers during the course of normal calls
- Securely authenticate customers with zero customer effort
- Reduce average handle time, no need for numerous security questions
- Significantly reduce fraud risk
Building a Knowledge Base
The beauty of AI and Machine Learning powered self-service applications means that they continuously learn and improve based on customer interactions. However, to get started self-service tools need to be trained and fed.
Working with a solution provider with sector specific knowledge can help shortcut a great deal of the front end of this process. FourNet’s sector specific expertise means we can help automate a large volume of simple queries using our sector specific templates that consolidate the most frequently asked questions or address the most common issues by industry sector. Responses to enquiries may include content that rarely changes where pre-trained answers from FAQ’s or workflows will guide customers and resolve their query accurately.
For more complex or tailored queries, the underpinning AI technology can be used to access more complex and dynamic content found in documents, knowledge bases, databases, product manuals, and business applications such as CRM & Service Desk.
Where answers are dynamic and constantly changing, the system can be trained to search through specific content that exists in different formats that are typically challenging for traditional search technology to interpret (PDFs, Excel tables, PowerPoint). With embedded AI, information can be intelligently labelled and indexed within your enterprise document library (headers, footers, content, images, tables) enabling smart discovery of precise answers from within bodies of text.
Where dynamic content is stored within databases, it will search information and content found in business applications such CRM systems, Service Desk, HR systems, databases or industry specific systems. Data can be retrieved to help identify customers for ID & V, and look-up content to provide users personalised responses.
Assisted Service
AI-assisted service provides agents with information that is tailored and relevant to the customer interaction they are having real-time whether by phone, chat or email. AI assistance is particularly useful for helping inexperienced agents, for remote working scenarios where asking colleagues is more difficult and for more complex interactions which may require multiple systems and databases to be accessed.
AI assisted service offers an opportunity to provide timely and effective support to every agent while the call is happening. AI can provide the agent with suggestions about next best action, pull up relevant information from the knowledge base, make suggestions based on customer history and use sentiment analysis to warn when a conversation is going off track. Real-time sentiment analysis can flag a supervisor remotely who can break into the conversation or whisper coach. These tools have a positive impact on first- contact resolution as well as customer experience.
AI assistance can help inexperienced agents where supervisors or experienced colleagues aren’t available, they improve the outcome of the interaction in real-time rather than waiting for post-call reviews.
Using natural language processing in real-time speech analytics can identify when an agent is experiencing stress, becoming emotional, or in need of whispered or direct intervention on a call.
Assisted Service technologies have never been more relevant during the pandemic where a high proportion of agents are working remotely. The positive impacts on performance, sickness and attrition for those agents who have adapted well to homeworking means that many contact centres will be pursuing a hybrid work strategy with some agents in the office and some working remotely. This makes AI Assisted Service technologies critical for businesses going forward
Smarter Routing & Operational Insights
Intelligent Routing
AI enabled contact centres can harness the huge processing power of AI to route queries to the right agent. The technology also helps make more streamlined decisions and use sentiment analysis to predict behaviour and improve outcomes.
Intelligent Routing utilises AI to automatically send inbound customer communications to the right place, so that best resource to deal with that customer query is allocated, thereby ensuring higher rates of First Contact Resolution. This can happen on any channel, whether phone, chat, text, email, or social media messaging. Not getting to the right resource the first-time results in agent handoffs which can require the customer to repeat themselves, all of which negatively impacts the customer experience.
A customer may begin engaging with the chatbot or IVR for self-service, but if they hit a dead end or need help from an agent, the chatbot or IVR leverages the data it has already gathered to route the customer to the best agent to resolve the issue.
Platforms based on machine learning ensure that the AI that drives intelligent routing learns from every customer interaction. This happens through feedback from both customers and agents, asking them how satisfied they are with how the customer was routed
Benefits
- Increased First Contact Resolution (FCR)
- Decreased Average Handle Time (AHT)
- More Personalized Customer Experience (CX)
- Increased Operational Efficiency
- Increased Customer Satisfaction and Sales
- Valuable Insights & Continuous Learning
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis is a way of quantifying customer and agent emotions within interactions, whether on the phone or through an alternate channel. Sentiment analysis captures and analyses every interaction, which is then scored on a sentiment scale from highly positive to highly negative. This can then be used to identify processes, behaviours and situations which cause strong levels of positive or negative sentiment that impact business outcomes and customer experience and enable root cause analysis to address and resolve the issue.
Using analytics and large data sources, datasets can be searched to identify and inspect the types of interaction that have major impacts on customer sentiment.
Uses of Sentiment Analysis
- Root cause analysis: by analysing thousands or millions of interactions, sentiment analysis is able to show the products, processes and topics which most often provoke the strongest negative or positive reactions.
- Quality assurance: sentiment analysis plays a part in quality management. Analysing metadata such as the topic under discussion should indicate whether this negativity arises from a specific agent performance or is more likely to be linked to the subject matter.
- Employee wellbeing: sentiment analysis can be used to understand and track agent morale and motivation. This is particularly relevant with the increase in remote working during the pandemic.
- Fraud detection: sentiment analysis can identify stress in real-time, which may be an indicator that fraud is taking place, prompting the agent to take the caller through more detailed levels of security in order to prove their identity.
Agent Efficiency
In today’s remote work environment, it’s more difficult than ever to understand how agents are performing. Supervisors have little direct oversight into an agent’s conversations, and it can be challenging to personalise coaching and understand which behaviours can be improved. AI for Quality Management is playing a huge role in managing agent performance. RPA is being harnessed in these post COVID times to free agent time and increase operational efficiency. Flexible scheduling has never been more critical as the entire nation adapts to rolling lockdowns, school closures, enforced quarantines and COVID related illness.
RPA
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can dramatically improve agent efficiency. RPA uses digital agents or ‘robots’ to handle repetitive, rules- based tasks with high accuracy and consistency, for example: assisting agents with change of address requests, ticketing processes, document reviews, and validating customer account information. RPA allows human agents to concentrate on more complex tasks.
Unlike AI, RPA robots carry out their tasks in a consistent manner each time, neither altering nor learning from their behaviour or past outcomes. RPA does not replace existing systems, instead they sit on top of existing logic and applications, using them in the same way that a human contact centre agent, chatbot or back-office worker would do. As such, RPA does not require complex integration, meaning roll-out of the robots can be relatively quick and flexible.
Most contact centres require agents to switch between multiple applications; hard enough in itself, let alone doing it while interacting with customers at the same time. RPA supports agents to assist customers by optimising the agent desktop. RPA-assisted integrated desktop solutions can remove the need for agents to log into multiple applications and can help them navigate between applications within the call. An RPA integrated desktop can ensure that customer data is gathered from the correct places and written back to any relevant databases without the need to navigate through multiple systems, rewrite systems or integrate deeply with multiple applications and databases. This both increases accuracy of data entry and frees the agent to focus on giving a great customer experience.
RPA can assist contact centres and back offices in numerous ways:
- Handling routine activities, e.g. change of address, automated login to specific systems, field completion, screen navigation, auto-filling information in other systems after an agent has entered it once.
- Validating customer account information.
- Proactively sending updates to customers depending on the stage of the process.
- Automatically trigger back-office processes based on rules set.
- Valuable Insights & Continuous Learning.
Workforce Management and Advanced Scheduling
“Unprecedented” makes it quite hard to predict what’s coming!
AI powered forecasting and scheduling tools have proven invaluable tools during the pandemic. The power of these tools allows contact centre managers or workforce planners to balance the increasingly complex scheduling requirements of a workforce faced with lockdown, quarantine and childcare and the changing demands of their customers.
Contact centres that are still running their scheduling on spreadsheets are struggling to cope with the increased range of variables required to accurately schedule agents given social distancing, multiple channels of customer communication and increased customer demands for round the clock support.
AI powered Workforce Management tools harness the processing power of AI to accurately forecast demand and schedule the appropriate levels of resource. They are powerful enough to cope with on-the-fly rescheduling that might be triggered by unexpected illnesses, childcare or quarantine requirements from employees or “unprecedented” peaks in demand from customers.
AI enabled forecasting and scheduling:
AI powered forecasting and scheduling tools have proven invaluable tools during the pandemic. The power of these tools allows contact centre managers or workforce planners to balance the increasingly complex scheduling requirements of a workforce faced with lockdown, quarantine and childcare and the changing demands of their customers.
- Enables forecasts and schedules to be run more frequently, easily and quickly; so managers can respond more quickly to peaks in demands and staffing fluctuations.
- Provides the option to reschedule easily, without having to start from scratch as would need to be done with a spreadsheet.
- Helps contact centre leaders to better assess forecast accuracy via visual reporting and rectify situations where the centre is over- or understaffed.
- Enables intraday changes to immediately improve the service level by making on- the-fly adjustments, such as optimising breaks and lunches.
- Makes it possible for supervisors and analysts to identify at a glance the best times to schedule off-phone activities to minimise the potential negative impact on customer service levels.
- Provides built-in communication services such as app notifications or SMS alerts to agents if schedules change.
Quality management
AI powered Quality Management empowers the contact centre to analyse and track agent performance across 100% of customer interactions. Insights and data can be used to inform general and individual training programs, mitigate compliance risk, and uncover business drivers for leadership.
Traditionally QM only analyses 1-2% of recorded voice calls; the manual processes and subjective scoring impacts on the quality of agent feedback and misses opportunities to improve the overall customer experience. With poor quality automation, call scoring, and as a result, suboptimal training programs, contact centres are missing out on the wealth of insights around customer sentiment and agent performance.
AI enables QM managers to analyse and score every voice call that takes place. With reduced manual input required, combined with machine learning intuitively surfacing critical insights and identifying gaps, QM teams can focus more on providing feedback and creating more relevant training programs.
Transcription services can transcribe hundreds of calls in minutes, enabling 100% call quality assurance and monitoring. Transcription services that are based on machine learning get better over time, and their capabilities grow as they encounter new types of data.
100%
call quality assurance and monitoring
Building the business case
If you're feeling whiplash, it might be the ten years forward we just jumped in 90 days' time.
McKinsey & Co.
The impact of the pandemic accelerated digital transformation at a pace never seen before. The early stages of lockdown, with the need to enforce social distancing or send contact centre employees home, led to long call wait times for many consumers. When digital became the default, many organisations realised that their self-service experiences weren’t up to scratch.
The need to cope with increased levels of demand with reduced levels of available agents has meant that organisations have been forced to look at how they can automate both for efficiency and to maintain the customer experience. As referenced in Figure 1 three of the top five drivers in investing in contact centre technology are driven by AI and automation objectives.
In this section we’ll help you articulate how investing in AI can help your contact centre save money, grow revenue, increase operational efficiency, innovate products and improve the customer experience.
Quantitative and Qualitative Benefits
Most contact centres will have comprehensive dashboards which measure their most important operational KPIs; we also recommend focusing on the human experience. Interview or work shadow your agents to understand their pain points and identify where they are spending their time. FourNet Business Analysts can help with this process, they can identify quick wins within the constraints of your current systems and provide you with the quantifiable potential benefits of streamlining these processes in terms of operational efficiency. The impact on employee engagement generated by enabling them to spend their time on helping customers rather than repetitive, inefficient processes is less easy to quantify but will have measurable results in terms of job satisfaction and retention.
When building the business case, prioritise the KPIs that executive decision-makers care about and connect them to financial value. For example, what would the financial impact be if assisted service could deliver the right content at the right time to your agents so that the average case handle time decreases by 10%? What would your average cost per contact look like if you could enable self-service on an additional 5% of inbound calls using natural language IVR? How much agent time could you save by handling 50% of your webchats using AI chatbots?
Below are some examples of how we’ve helped our customers use AI to save money, grow revenue, increase operational efficiency, innovate and improve the customer experience
Save Money
- Recent projects have seen up to a 43% reduction in the volume of live chat requests that can now be handled by AI virtual assistants.
- Quantify the number of simple queries that could be answered by chatbots or voicebots, identify your contact centre’s cost per inbound contact and model the impact that this switch in types of contact has on your overall cost to serve.
Increase Operational Efficiency:
Reduce Average Handle Time (AHT);
- AI powered Assisted Service for Agents can reduce the average handle time per
call by suggesting best-next-action or pulling up relevant information from the knowledge base. This reduces the need for screen switching and streamlines the call. - Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can have a dramatic impact on Average Handle Times. Using RPA-assisted integrated desktop solutions saves agent time switching between screens during the call and reduces Call Wrap-Up times post call by ensuring data is written back to any relevant databases.
- Average Handle Time for webchat can be reduced to zero agent hours for those queries that can be handled by AI chatbots.
Increase First Contact Resolution (FCR);
- Intelligent Routing ensures that queries are directed to the right agent to handle the customer’s specific issue. Making AI powered decisions based on the caller identity, customer journey input and data already gathered via chatbot or IVR can route the contact to the agent best suited to resolve the issue. We have seen increases in FCR of up 20% after implementing AI powered Intelligent Routing solutions.
- Assisted Service can have a dramatic impact on FCR rates as well as Average Handle Times, we’ve seen improvements of nearly 20%.
Grow Revenue:
Increased retention rates;
- There are multiple research sources that have proven the link between increased Customer Satisfaction and higher retention rates. According to Invesp, improving customer retention rates by just 5% can increase profits by between 25% and 95%. Using the average Life Time Value (LTV) of a customer you can model the impact that even small percentage increase in retention would have on the bottom line.
Increased retention rates;
- Assisted Service can use AI to suggest relevant cross-sell or upsell options to the agent while on the phone.
Improve the Customer Experience
A study by Aurora Market Research into 1,000 UK consumers commissioned by Contact Babel identified the most important factors to a customer when contacting an organisation:
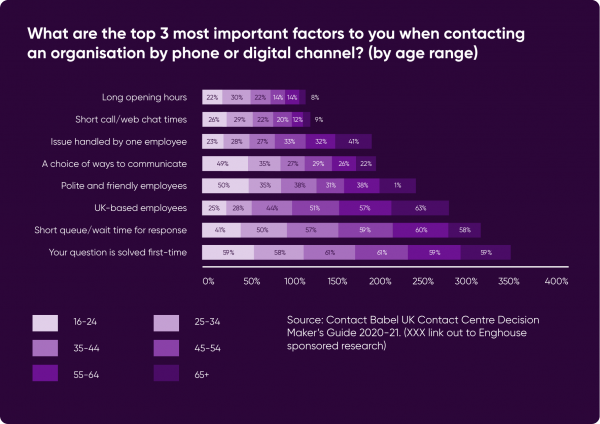
First contact resolution and a short wait time for a response were the top two most important criteria across all age groups (apart from UK-based employees for the over 65s) showing that the increased FCR, enable self-service and reduce handle times benefits delivered by AI will contribute strongly to the overall customer experience.
Getting started
The great thing about AI in the age of cloud and as-a-service technology is that you don’t have to take an all or nothing approach to the trend.
In fact, we strongly recommend most organisations make decisions with the long term in mind but start with small projects. By this we mean that for those organisations looking to upgrade their overall contact centre infrastructure, now is the time to look at solutions built with AI at the heart which will provide a framework on which to build for the future. But for organisations who are not undertaking large contact centre system upgrades and those organisations with existing estates, we recommend you start with a small self-contained project for a clearly defined business issue or process e.g. chatbots to replace digital enquiries.
It is important that the boundaries of the project are clearly defined and understood, with relevant baseline metrics captured before the project, and clear and achievable outcomes defined so the success of the project can be clearly measured. A limited, low-risk use case that can be simply implemented can demonstrate a quick win to build confidence in using AI within the contact centre.
While quick wins are essential to get buy-in, it is essential to place the project in the context of a longer-term vision. We recommend building a roadmap of linked businesses cases that layout a long-term vision for the strategic use of AI across all customer facing parts of the organisation.
How FourNet can help
Building the business case
FourNet Business Analysts can help you build your business case to demonstrate ROI and payback periods based on your current costs and KPIs. Get in touch to schedule an initial discovery call.
AI powered chatbots
AI powered chatbots can deliver significant cost savings by diverting inbound enquiries away from the contact centre and enabling the customer to self-serve thus freeing agent time. As well as improving customer satisfaction, organisations implementing AI chatbots are seeing payback periods within months.
Regardless of what installed technology you are using FourNet have a range of solution partners who interoperate with your existing contact centre, CRM and enterprise applications to deliver fully integrated chatbot solutions that can be rolled out in weeks and paid back in months.
Cutting-edge customer experience
FourNet work with the world's leading Cloud Contact-Centre-as-a-Service vendors to digitally enable every channel to give a great customer experience. These cutting-edge technology solutions utilise AI to enable customers to self-serve, to route queries to the right agent every time and to automatically complete routine customer interactions and after-contact work thus freeing agent time to focus on adding value to the customer.
Every requirement is different: from customer expectations to strategic business objectives and from installed legacy technology to budgetary constraints; FourNet have a range of solutions to help so please get in touch to find out how we can help.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA can automate repetitive tasks that are currently performed by agents or employees to deliver dramatic operational efficiencies and cost savings. The challenge has always been knowing where to start. Selecting the right processes to automate has historically been time consuming and has relied on manual analyses based on subjective judgements.
FourNet can offer a free proof-of-concept Automation Finder trial for selected customers which can identify process sequences with the biggest ROI potential based on frequency, volume and handle time. Installed on a selection of agent or employee desktops Automation Finder captures and tracks their day-to-day tasks and desktop activities including keystrokes, mouse selections, applications used, pages visited, field entries, handle time, and more. Utilising Machine Learning to classify employee data into meaningful actions, it also tracks the handle time for these actions; Automation Finder can then identify activities with the largest ROI potential for automation.
Automate connectivity
Automation offers cost savings and operational efficiencies at every level of the technology stack. FourNet's secure network infrastructure is built on the UK's most innovative carrier network, utilising automation to reduce service lead times from days to minutes to drive down costs by speeding up deployments and enabling customers to flex bandwidth on demand.
Whether you're opening a new site, responding to ongoing needs to switch employees between office and home or flexing to peaks and troughs in demand; FourNet managed network services provides flexibility and security to respond to whatever your business demands. With immediate visibility of connectivity options, near real-time configuration of circuits and direct API ordering links into all the major carriers we can help our customers respond to rapidly changing market conditions.
AI powered security
Digital transformation, hybrid working, new applications: the attack surface grows dramatically making security management increasingly difficult. Internal security teams struggle to keep up with the deluge of alerts and other information generated by their multitude of security devices. And the cybersecurity skills gap only makes this more difficult.
FourNet work with Fortinet, the number 1 cybersecurity firm in the world, who utilise AI and and ML to process and analyse more than 10B events every day, sending actionable real-time threat intelligence to our customers.
Want to discuss your AI and Automation challenges?
Our AI and Automation experts can help you to deliver your operational efficiency, customer experience and employee engagement goals.


